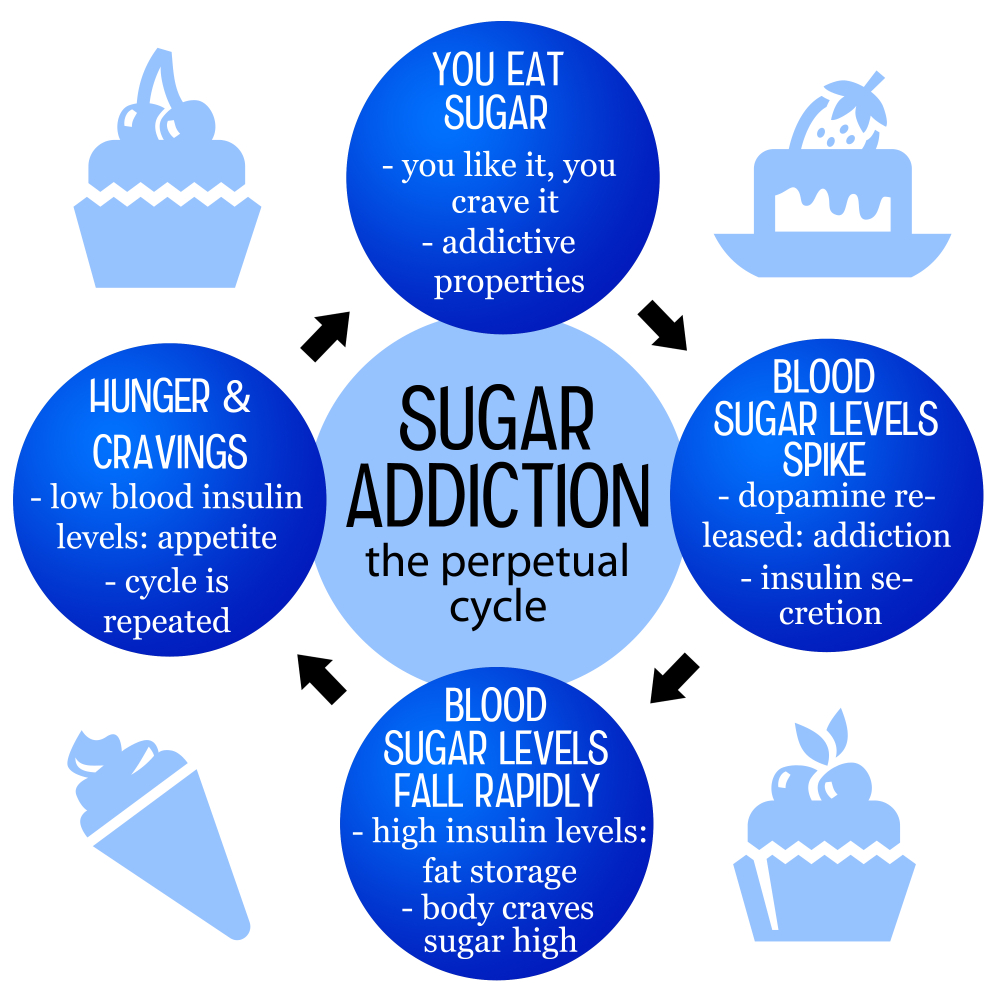
Is sugar addictive? This intriguing question has sparked considerable debate among health experts and nutrition researchers alike. While sugar does trigger cravings similar to those caused by substances like alcohol and nicotine, it doesn’t meet the stringent clinical criteria to be labeled as an addictive substance. However, the health effects of sugar can lead to compulsive eating behaviors, especially with the prevalence of processed foods packed with added sugars. With an average of 20 teaspoons consumed daily by Americans, understanding sugar addiction and its impact on our wellbeing is more important than ever.
The allure of sweet treats has some researchers comparing the nature of sugar cravings to those associated with other highly sought-after substances. Although sugar is often seen as simply a delightful element of our diets, its propensity to encourage repeated consumption blurs the lines between normal dietary habits and a more complex relationship resembling addiction. Processed foods are notorious for their added sugars, which can significantly alter our physiological responses and influence our eating patterns. This situation raises concerns about the long-term health effects of sugar on our bodies, making it essential to explore how our bodies manage such ingrained cravings.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a term used to describe the compulsive behavior of consuming sugar-laden foods and drinks, which can lead to intense cravings. Many nutrition experts note that while sugar can lead to increased dopamine release in the brain, similar to other addictive substances, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria of addiction. Unlike alcohol and drugs, sugar is an essential part of many natural foods, including fruits and dairy. This makes the categorization of sugar as an addictive substance controversial, causing significant debate among researchers.
The context of sugar within processed foods further complicates the understanding of its addictive nature. The convenience and palatability of ultra-processed foods often lead to habitual overconsumption. This cycle can create strong cravings and emotional attachments to sugary treats, making it challenging for individuals to control their intake. Recognizing the difference between a dietary necessity and a potentially harmful addiction is crucial for addressing sugar cravings in a healthy and balanced manner.
Health Effects of Excess Sugar Consumption
The health effects of sugar are multifaceted and can lead to significant physical and psychological impacts. Excessive sugar consumption is linked to various health problems, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. With the average American consuming around 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, it is evident that many are unaware of the recommended limits set by health organizations. Reducing sugar intake can improve overall health outcomes and diminish the risk of developing chronic diseases that stem from high sugar consumption.
Moreover, the psychological effects of sugar can be just as concerning. People often report experiencing mood swings and cravings when they consume high amounts of sugar, which can mimic withdrawal symptoms associated with addictive substances. These reactions highlight the importance of being mindful about sugar consumption, especially concerning the hidden sugars in processed foods. Helping individuals understand how to read food labels can empower them to make healthier choices and reduce reliance on sugar for emotional comfort.
Sugar Cravings: Causes and Solutions
Sugar cravings can stem from various factors, including emotional stress, habitual eating patterns, and the addictive properties of sugar-rich processed foods. When individuals consume large amounts of sugar, their bodies can develop a dependence on it, leading to cravings when sugar levels drop. These cravings are often exacerbated by emotional triggers, making it vital to identify underlying causes to manage intake effectively.
To combat sugar cravings, it’s recommended to gradually reduce sugar intake rather than quitting abruptly. A sudden drop can often result in withdrawal-like symptoms, making it difficult for individuals to stick to their goals. Finding healthier alternatives, such as naturally sweet fruits and whole foods, can satisfy sweet tooth cravings without the negative consequences of added sugars. A balanced diet, rich in nutrients, can also help stabilize mood and energy levels, ultimately reducing cravings for sugar-laden processed foods.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Addiction
Processed foods play a significant role in the prevalence of sugar addiction, as they often contain high amounts of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. These ingredients are specifically chosen to enhance flavor and texture, making the foods more appealing and difficult to resist. The marketing of such foods often targets emotional triggers, creating a cycle of consumption that can lead to habitual overeating and sugar dependency.
Understanding the relationship between processed foods and sugar addiction is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet. By opting for whole, unprocessed foods, individuals can avoid excessive sugar intake and promote better health overall. Cooking meals from scratch and paying attention to ingredient labels can empower consumers to make informed choices and break the cycle of sugar cravings caused by processed food consumption.
Navigating Sugar Consumption for Better Health
Navigating sugar consumption requires a balanced approach that considers both the psychological and physical aspects of sugar intake. Moderation is key; enjoying sweets occasionally can be part of a healthy lifestyle. The American Heart Association recommends specific daily limits for added sugar, emphasizing the need for awareness among consumers about their sugar intake. Individuals should prioritize whole foods while being cautious of hidden sugars in snacks and beverages.
Additionally, creating a positive relationship with food means understanding that it’s okay to enjoy sweet treats in moderation without guilt. Healthier alternatives, like fruit-infused water or yogurt with natural sweeteners, can satisfy sweet cravings without excessive added sugar. Establishing sound eating habits and being conscious of the sources of sugars can lead to better overall health and a more enjoyable experience with food.
Debunking Myths Around Sugar and Addiction
There are various myths surrounding sugar and its potential for addiction, with some suggesting that sugar is as addictive as hard drugs. It’s essential to clarify that while sugar does trigger pleasure responses in the brain, it does not create the same severe dependency seen with substances like alcohol or opioids. Understanding these misconceptions allows individuals to approach their sugar consumption with more realistic expectations and healthier perspectives.
Debunking these myths is vital for encouraging people to enjoy sugar responsibly without fear of an addiction label. Education on the physiological effects of sugar can help individuals recognize the importance of moderation rather than total restriction, often leading to healthier long-term habits. Instead of viewing sugar as solely an enemy, it can be appreciated as part of a diverse and balanced diet.
How to Manage Sugar Intake Effectively
Managing sugar intake effectively involves making conscious decisions about food choices and understanding serving sizes. By becoming familiar with nutrition labels, individuals can keep track of their sugar consumption and ensure they are staying within recommended limits. Being informed about hidden sugars in everyday products can help minimize extra calories and health risks associated with excessive sugar intake.
Incorporating strategies such as meal prepping and planning can also assist in managing sugar consumption. Preparing healthy snacks and meals in advance can prevent impulsive eating and reliance on sugary convenience foods. Finding support through meal plans or health blogs focused on reducing sugar can empower individuals on their journey toward healthier eating habits.
The Importance of Gradually Reducing Sugar Intake
When addressing sugar consumption, it’s crucial to gradually reduce intake rather than opting for extreme dietary changes. Abruptly eliminating sugar can lead to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms, including mood swings and increased cravings. Instead, a gradual reduction allows the body to adjust, making it easier to shift dietary habits without feeling deprived.
Setting realistic goals, such as decreasing added sugars incrementally over time, can lead to sustainable and long-term changes. Additionally, substituting sugary foods with healthier alternatives can aid in this transition. By making gradual adjustments, individuals can reduce their sugar intake without losing enjoyment in their eating experiences, ultimately creating a healthier relationship with food.
The Positive Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
While excessive sugar intake has health implications, it’s also vital to acknowledge the role sugar plays in a balanced diet. Natural sugars found in fruits and dairy products provide essential nutrients and energy necessary for maintaining overall health. These sugars are part of a range of foods that contribute to dietary variety and enjoyment.
Understanding that not all sugars are equal is essential. The focus should be on limiting added sugars while still appreciating the natural sweetness found in whole foods. This balanced approach can help individuals maintain a nutritious diet without feeling deprived, allowing for the enjoyment of sweet flavors within a health-conscious framework.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like drugs or alcohol?
The debate over whether sugar is addictive is ongoing. While sugar does trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine according to clinical criteria. The accessibility of sugar in ultra-processed foods can lead to habitual consumption, creating withdrawal-like symptoms when discontinued, but these symptoms are generally less severe.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can result in negative health effects such as increased cravings, compulsive eating, and potential psychological impacts like anxiety and irritability during withdrawal. Excessive sugar consumption is linked to numerous health issues, including obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Thus, moderation is key in managing sugar intake.
How do sugar cravings develop?
Sugar cravings often develop due to the consumption of ultra-processed foods high in added sugar. These foods are designed to be highly palatable, creating a desire for more. When one reduces sugar consumption significantly, they may experience withdrawal symptoms, which can intensify cravings for sugary foods.
Are all sugars the same when considering sugar addiction?
Not all sugars are the same. Naturally occurring sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy are different from added sugars found in processed foods. While we need some sugar for energy and flavor, added sugars, particularly in high amounts, are linked to unhealthy eating behaviors and can contribute to sugar addiction-like symptoms.
What is the recommended daily sugar intake to avoid sugar addiction?
To minimize the risk of sugar addiction and its health effects, the American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to 9 teaspoons (36 grams) for men and 6 teaspoons (25 grams) for women daily. For children, less than this is advised, emphasizing the importance of reading food labels and being aware of sugar content.
Can reducing sugar intake help with sugar addiction?
Yes, gradually reducing sugar intake can help manage cravings and decrease dependency. Going ‘cold turkey’ may backfire for some, leading to increased cravings. A gradual reduction allows the body to adjust and can facilitate healthier eating patterns without severe withdrawal symptoms.
How does sugar consumption relate to processed foods and addiction?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them more appealing and harder to resist. This leads to habitual consumption and the potential for sugar addiction-like behaviors, as repeated exposure reinforces cravings and increases the desire for these foods.
Are there alternative approaches to managing sugar cravings?
To manage sugar cravings, consider incorporating more whole foods into your diet, including fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Hydration, balanced meals, and mindful eating practices can also help reduce cravings and foster healthier relationships with food.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of Addiction | Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine but can trigger cravings and compulsive behaviors. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | People may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when reducing sugar intake. |
| Food vs. Substance | Sugar is present in many essential foods and is not something that can be completely eliminated from the diet. |
| Average Sugar Consumption | The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, exceeding recommended limits. |
| Health Recommendations | American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
| Gradual Reduction | It’s advisable to reduce sugar intake gradually rather than abruptly to avoid negative effects. |
| Role of Sugar in Diet | Moderate sugar intake can enhance flavor and pleasure in food, which is beneficial. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? While sugar can stimulate cravings similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as such in clinical terms. Research indicates that high consumption of sugar-loaded, ultra-processed foods can lead to compulsive eating and potential withdrawal symptoms, yet sugar remains an essential nutrient found in many healthful foods. Experts suggest that moderation is key, with specific recommendations from health organizations to limit added sugar intake effectively. Thus, understanding sugar consumption and making gradual reductions is vital for promoting healthier eating habits without risking harsh withdrawal reactions.