Suicide prevention for older adults has become a pressing concern, as this demographic faces significantly higher suicide rates than younger counterparts. Recent studies indicate that seniors, particularly those aged 75 and older, experience unique mental health challenges that contribute to their risk, such as social isolation and bereavement. Despite these alarming statistics, there is a glaring lack of accessible suicide prevention resources tailored specifically for the elderly population. As healthcare professionals in geriatric psychiatry continue to work with older adults expressing suicidal thoughts, it has become crucial to enhance the awareness and availability of online resources for seniors. By addressing this urgent need, we can establish robust suicide prevention initiatives that prioritize mental health and improve overall well-being for older adults.
Addressing the issue of elderly suicide rates is a critical aspect of mental health care, particularly for seniors facing the challenges of aging. With the demographic shift towards an older population, there is a growing realization of the need to focus on the mental health of older individuals, who often grapple with feelings of loneliness and despair. It is essential to recognize and develop effective suicide prevention resources that meet the distinct needs of this age group. Furthermore, exploring alternative methods of support, including online initiatives and community outreach, can greatly enhance the availability of help for those at risk. As we delve deeper into this topic, it becomes evident that tailored suicide prevention strategies are paramount to safeguarding the emotional well-being of our elderly population.
Understanding the High Risk of Suicide Among Older Adults
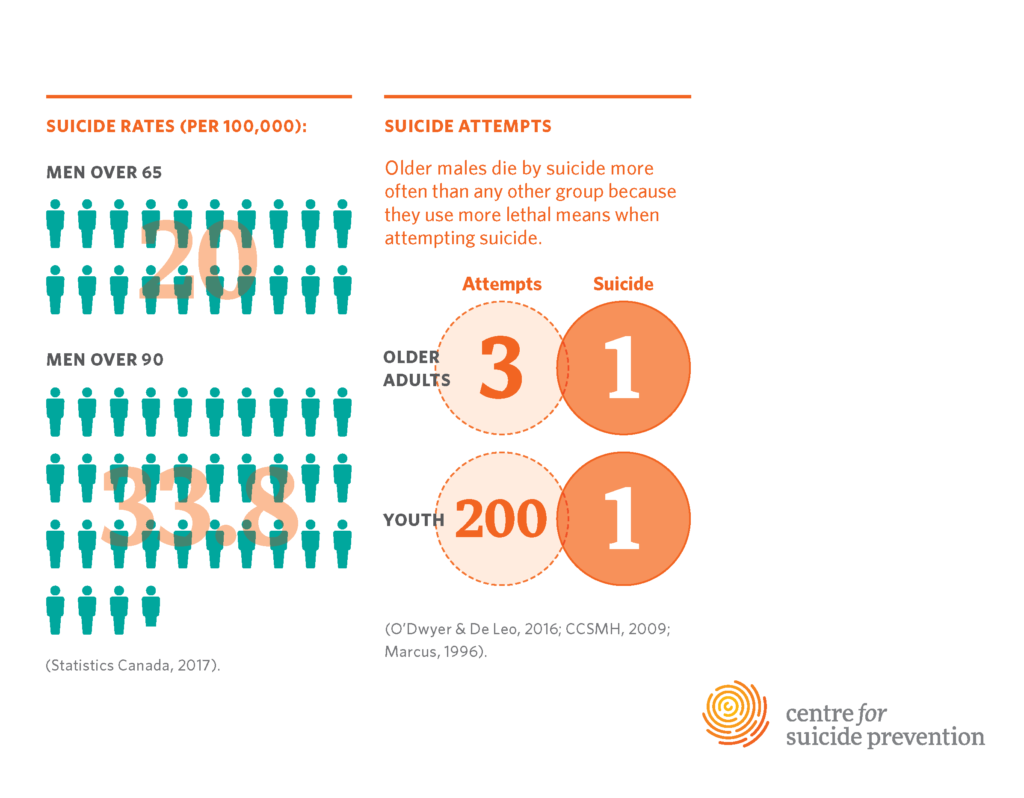
As we examine the complex landscape of mental health for older adults, it becomes evident that this demographic faces unique challenges that significantly elevate their risk for suicide. Research from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention illustrates that individuals aged 75 and older experience a suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000, a stark contrast to declining rates in younger populations. This alarming statistic calls attention to the need for specialized mental health resources aimed at older adults, who may often encounter barriers such as health conditions, social isolation, and lack of support systems.
The reasons contributing to the elevated suicide rates include loneliness and social exclusion, which are prevalent among older adults, especially those living alone. Moreover, the underrepresentation of older adults in mental health research often results in a lack of targeted suicide prevention resources. Addressing these issues through dedicated campaigns focusing on the mental health of seniors is crucial. This could involve not only enhancing accessibility but also tailoring messages that resonate with older individuals’ lived experiences.
The Role of Online Resources for Seniors in Suicide Prevention
In today’s digital age, the internet serves as a critical resource for individuals seeking mental health support, including seniors at risk of suicide. However, studies have shown that online resources specifically designed for older adults are alarmingly sparse. This gap in resource availability was highlighted by recent research conducted at McLean Hospital, which revealed that many established suicide prevention organizations do not cater to the unique needs of older adults. While these organizations recognize the increased suicide risk among this population, their online presence often fails to provide user-friendly and accessible information.
Integrating easily navigable online platforms that focus on mental health for the elderly is essential. These resources should offer tailored interventions that consider the physical limitations, cognitive changes, and social circumstances faced by older adults. In moving forward, it is vital for organizations to reassess their online strategies, employing geriatric psychiatry practices to ensure that resources are not only available but also effective for this vulnerable demographic.
Geriatric Psychiatry: A Key Player in Suicide Prevention
Geriatric psychiatry stands at the forefront of addressing mental health concerns among older adults, especially regarding suicide prevention. Specialists in this field are uniquely trained to understand and address the intricacies of mental health issues that affect seniors, such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. By focusing on these issues, geriatric psychiatrists can offer comprehensive assessments and develop individualized treatment plans that align with an older adult’s specific healthcare needs.
Moreover, the field of geriatric psychiatry emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in supporting older adults. Collaborating with primary care providers and community organizations can enhance the reach of suicide prevention efforts, ensuring that older individuals receive holistic care that aids in addressing not only their mental health needs but also the social factors contributing to their risk. This collaborative effort is critical for creating a supportive framework that protects the mental wellbeing of seniors.
Identifying Suicide Prevention Resources for Aging Individuals
The challenge of finding adequate suicide prevention resources tailored for older adults cannot be overstated. Traditional resources often overlook the nuanced needs of seniors, leading to a significant gap in accessible information. Recent studies indicate that while suicide prevention organizations recognize the vulnerability of older adults, their initiatives frequently miss the mark in terms of direct outreach and resource distribution. This oversight can have dire implications for seniors who may not know where to turn in times of crisis.
To enhance the availability and effectiveness of these resources, it is paramount that we implement campaigns explicitly aimed at older adults. These initiatives should promote awareness and educate both seniors and their families on how to identify warning signs, seek help, and utilize available mental health services. Creating easily accessible online platforms that compile information on suicide prevention resources specifically for the elderly can empower this demographic and connect them to necessary support systems.
The Impact of Social Isolation on Elderly Suicide Rates
Social isolation is a significant factor influencing the mental health of older adults, contributing notably to increased suicide rates within this age group. Many seniors reside alone or have limited social interactions, which can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and despair. Understanding the detrimental effects of social isolation is crucial for developing effective suicide prevention measures tailored to this demographic. Recognizing that strong social connections can serve as protective factors highlights the importance of community engagement in mental health initiatives for older adults.
Encouraging programs that foster social connections among seniors, such as community centers, volunteering opportunities, and peer support groups, can provide essential social interaction and reduce feelings of isolation. Furthermore, integrating these social initiatives within broader suicide prevention strategies enhances their effectiveness. By combating social isolation, we can create a more supportive environment that promotes mental health and wellbeing for older adults.
Combatting Ageism in Mental Health Awareness
Ageism remains a significant barrier to effective mental health care and suicide prevention for older adults. Misconceptions about aging often lead to the stigmatization of mental health issues within this demographic, causing many seniors to hesitate in seeking help. Addressing ageist attitudes is essential for creating an environment that values the mental health of older adults, validating their experiences and struggles. Educational campaigns aimed at dispelling myths about aging and mental health can help combat these stereotypes.
Moreover, advocating for policies that prioritize mental health services for older adults can help in reducing the stigma associated with seeking help. By fostering a culture that encourages open discussions about mental health and emphasizes the importance of prevention resources tailored for seniors, we can initiate a significant change in how society perceives and supports the mental wellbeing of older adults.
The Need for Policy Changes in Suicide Prevention
To effectively address the rising rates of suicide among older adults, substantial policy changes are necessary to enhance mental health resources available to this population. Current frameworks often overlook the unique healthcare needs of seniors, and policymakers must prioritize the establishment of comprehensive strategies that enhance access to geriatric psychiatry services. Implementing funds specifically aimed at research and intervention programs for late-life mental health issues can lead to profound improvements in suicide prevention efforts.
Additionally, crafting policies that increase funding for community-based resources tailored for older adults is essential. These resources must be easily accessible and designed with the elderly in mind, ensuring that they resonate with their experiences and barriers. Policymakers must listen to the voices of will-be stakeholders, including seniors themselves, to create impactful change that adequately meets the needs of this vulnerable population.
Utilizing Technology to Enhance Mental Health Resources
Technology presents a unique opportunity to enhance mental health resources for older adults, particularly in suicide prevention. With the growing prevalence of digital literacy among seniors, it’s vital to leverage technology to create intuitive platforms that offer pertinent mental health resources. Utilizing telehealth services can significantly reduce barriers to access, allowing older adults to receive support from the comfort of their homes. Innovative applications that provide immediate access to suicide prevention resources, online therapy, or support groups can prove invaluable.
Furthermore, technology can bridge the gap in reaching out to isolated seniors. Regular text messages, reminders, or alerts about available resources and check-in services can maintain an ongoing connection. By integrating technology into mental health care, we can facilitate timely interventions, empowering older adults to access the help they require and decreasing the likelihood of crisis situations.
Community-Based Initiatives for Suicide Prevention in Seniors
Community-based initiatives play a crucial role in suicide prevention for older adults by fostering environments that promote mental well-being. Local organizations and health care systems can mobilize resources to create supportive networks that actively engage seniors. Familiarizing older adults with resources available in their communities, such as counseling services, peer support groups, and recreational programs, can help combat the feelings of isolation that contribute to their increased suicide risk.
These initiatives can also provide training for community members and caregivers to recognize warning signs and address the topic of mental health openly. By building a collaborative approach that includes families, friends, and care providers, communities can create a safety net for older adults, ensuring they feel supported and less alone in their struggles. Through these engagements, we can work towards diminishing the stigma around mental health and reinforce a community’s role in safeguarding the mental well-being of its senior members.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common factors contributing to suicide among older adults?
Older adults often face unique challenges that increase their suicide risk, including social isolation, chronic illness, loss of loved ones, and mental health issues. Understanding these factors is crucial in developing effective suicide prevention strategies for older adults.
How can family members help in suicide prevention for older adults?
Family members can be instrumental in suicide prevention for older adults by recognizing warning signs, fostering open communication, encouraging professional help, and actively engaging in their emotional well-being and social activities.
What online resources are available for suicide prevention specifically targeting older adults?
There are several online resources available for suicide prevention aimed at older adults, including the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline, the Suicide Prevention Resource Center, and organizations focused on elder mental health, providing information and support tailored to seniors.
What role does geriatric psychiatry play in suicide prevention for older adults?
Geriatric psychiatry plays a vital role in suicide prevention for older adults by addressing their specific mental health needs through tailored treatments, therapy, and medication management, ultimately improving their overall quality of life.
How can community programs support suicide prevention for older adults?
Community programs can support suicide prevention for older adults by offering social engagement activities, mental health workshops, and easily accessible resources that promote mental health awareness and provide support networks.
What impact does social isolation have on elderly suicide rates?
Social isolation significantly impacts elderly suicide rates as it can lead to feelings of loneliness and despair. Programs that encourage community interaction and support can mitigate this risk and promote mental health.
What steps are being taken to improve suicide prevention resources for older adults?
Efforts are underway to improve suicide prevention resources for older adults, including advocating for targeted campaigns, increasing funding for research in late-life suicide prevention, and ensuring that resources are easily accessible online.
How do mental health conditions contribute to suicide risk in older adults?
Mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety can heighten the risk of suicide in older adults. Addressing these issues through accessible mental health care can be vital in suicide prevention.
What initiatives exist for improving elderly mental health and reducing suicide risk?
Various initiatives aim to improve elderly mental health and reduce suicide risk, such as raising awareness about the mental health needs of older adults, developing tailored intervention programs, and increasing research funding in geriatric psychiatry.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Population at Risk | Older adults, especially those aged 75 and older, have the highest suicide rates. |
| Resource Availability | National suicide prevention organizations have limited resources aimed at older adults. |
| Study Findings | Research shows an imbalance in online suicide prevention efforts, not addressing older adults’ needs. |
| Importance of Action | There’s an urgent need for campaigns and resources that are easily accessible to older adults. |
| Contributing Factors | Social isolation, loneliness, and systemic biases contribute to higher suicide rates in older populations. |
| Call to Action | More funding and research for late-life suicide prevention are necessary. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue that requires immediate attention and action. The alarming statistics indicate that adults aged 75 and older are particularly vulnerable to suicide, yet they face significant barriers in accessing necessary resources. This indicates a clear need for tailored and accessible suicide prevention campaigns that consider the unique healthcare challenges older adults encounter. By addressing these disparities and increasing awareness, we can create an environment that promotes mental well-being and supports our elderly population in crisis.